The Hidden Costs of Poor Refrigeration Monitoring (and How to Avoid Them)
When it comes to industries like food service, pharmaceuticals, and cold storage logistics, refrigeration monitoring is not just a technical upgrade — it’s a necessity. Poor monitoring systems (or none at all) can quietly drain thousands of dollars from your business through product loss, increased energy bills, and regulatory fines.
In this post, we’ll explore the hidden costs of poor refrigeration monitoring, real-world examples of what can go wrong, and most importantly — how to avoid these costly mistakes.
Why Refrigeration Monitoring Matters
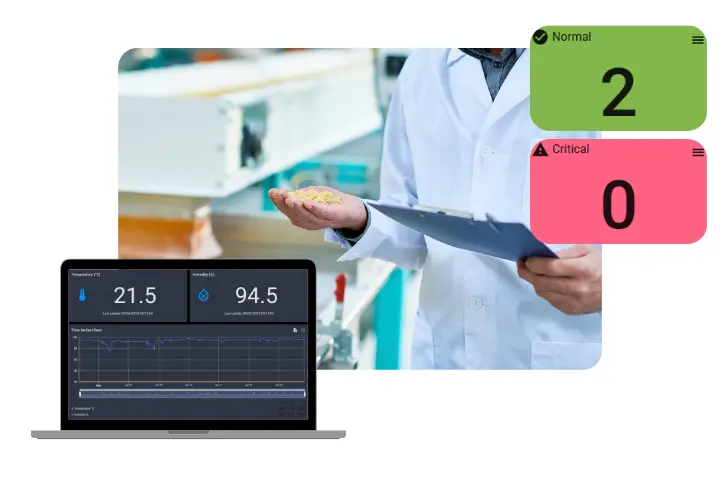
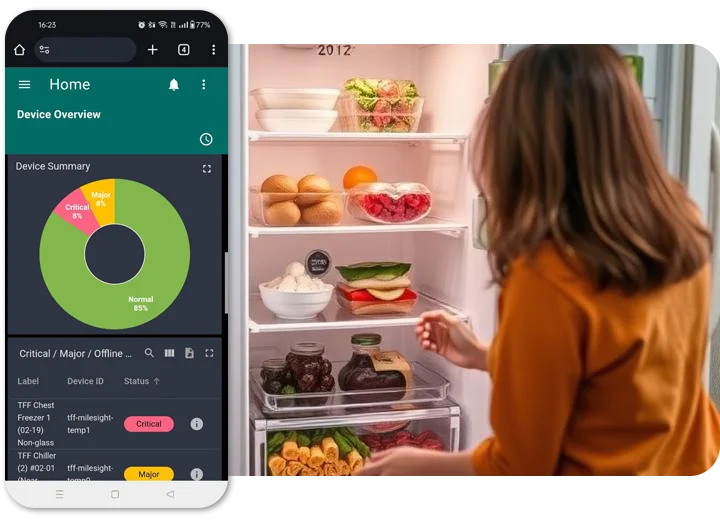
Refrigeration monitoring involves the use of sensors, software, and alerts to track temperature, humidity, and performance metrics in cold storage units.
A modern system will:
- Track temperature fluctuations in real-time
- Send instant alerts for out-of-range readings
- Keep data logs for compliance audits
- Help reduce energy consumption
But what happens when your system isn’t up to par — or worse, you have no system at all?
1. Product Loss: A Silent Profit Killer
If your refrigeration fails overnight and no one knows, the damage can be irreversible by morning. In food and pharma industries, even a few degrees of deviation can result in spoiled inventory.
💸 Real Cost Example:
- A restaurant loses $5,000 in meat and dairy due to an unnoticed overnight failure
- A medical lab discards $20,000 worth of temperature-sensitive vaccines
These losses aren’t always covered by insurance and can erode margins fast.
2. Compliance Failures and Legal Risks
Industries regulated by FDA, USDA, or CDC require strict temperature logging and storage protocols.
Without a reliable refrigeration monitoring system, your business could face:
- Failed inspections
- Product recalls
- Fines or even license suspension
✅ How Monitoring Helps:
Alerts help prevent violations before they happen
Automatic logging meets regulatory standards
Digital audit trails reduce manual errors
3. Increased Energy Consumption
Poor monitoring doesn’t just risk your inventory — it costs you on your utility bill too.
Without real-time insights:
- Units may run colder than necessary
- Door seals and compressors may be working overtime
- You miss early signs of inefficient performance
Energy-efficient refrigeration depends on knowing how your equipment is behaving. Monitoring systems help you tune performance and spot inefficiencies before they become expensive problems.
4. Unplanned Downtime & Emergency Repairs
A single malfunctioning compressor can halt operations for hours or days — especially if it happens on a weekend or holiday.
With no proactive alerts or diagnostics, you’re always reacting too late.
🚨 What Monitoring Prevents:
Damaged brand reputation from missed deadlines
Emergency repair fees
Delayed production or order fulfillment
5. Labor and Operational Inefficiency
Manually checking and logging temperatures is:
- Time-consuming
- Error-prone
- Not scalable for multi-unit operations
Modern refrigeration monitoring systems automate all of this, freeing your staff to focus on high-value tasks. Plus, with centralized dashboards, you can monitor multiple locations from a single platform.
How to Avoid These Hidden Costs
✅ Invest in a Smart Refrigeration Monitoring System
Look for solutions that include:
- Real-time temperature tracking
- Remote access via mobile or desktop
- Automated alerts via SMS/email
- Cloud-based data storage for audits
- Energy usage analytics
✅ Set Alert Thresholds
Customize your temperature thresholds based on the product type. For example:
- Fresh produce: 32°F to 40°F
- Vaccines: 35°F to 46°F
✅ Train Your Team
Ensure your staff:
- Knows how to respond to alerts
- Understands the importance of refrigeration logs
- Follows SOPs for emergency situations
✅ Perform Routine Maintenance
Monitoring alerts are only useful if equipment is maintained. Use the data to identify failing components early and schedule preventative service.