Do You Need a Wi-Fi or Cellular Temperature Data Logger? Here is How to Choose
Monitoring temperature-sensitive products is a critical task across various industries such as healthcare, pharmaceuticals, food storage, logistics, and environmental monitoring. To perform this effectively, you need a reliable temperature data logger.
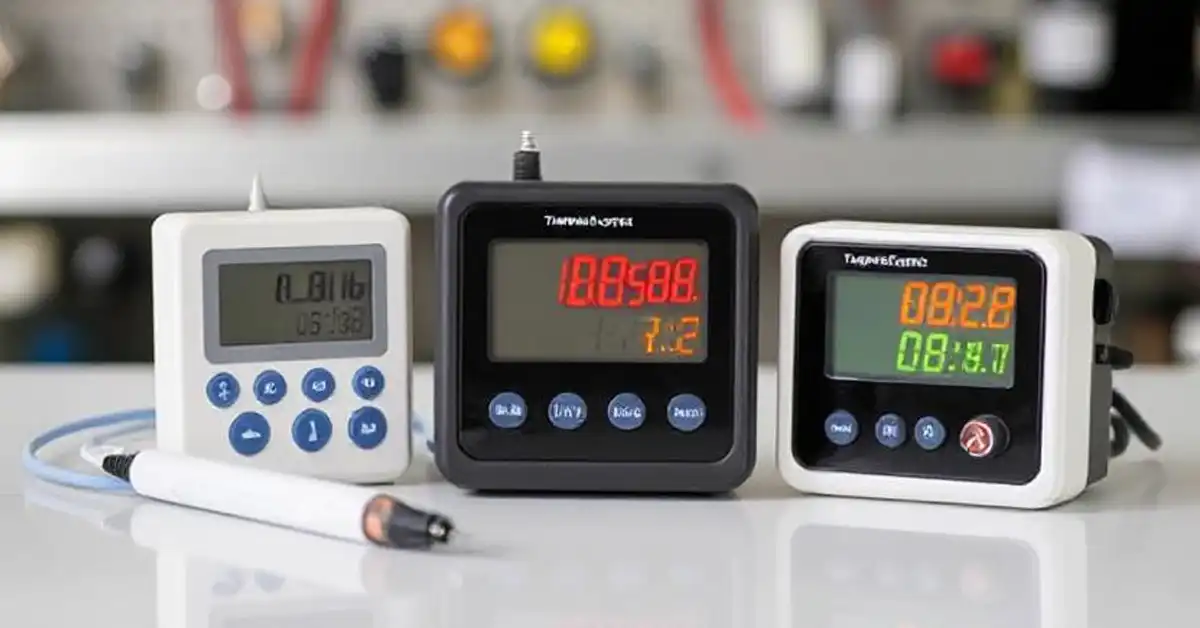
Modern temperature data loggers now offer advanced connectivity options, mainly Wi-Fi and cellular. Each type has its own advantages, depending on your operational needs, environment, and data access requirements.
This guide will help you understand the key differences between Wi-Fi and cellular temperature data loggers so that you can make an informed decision.
What Is a Temperature Data Logger?
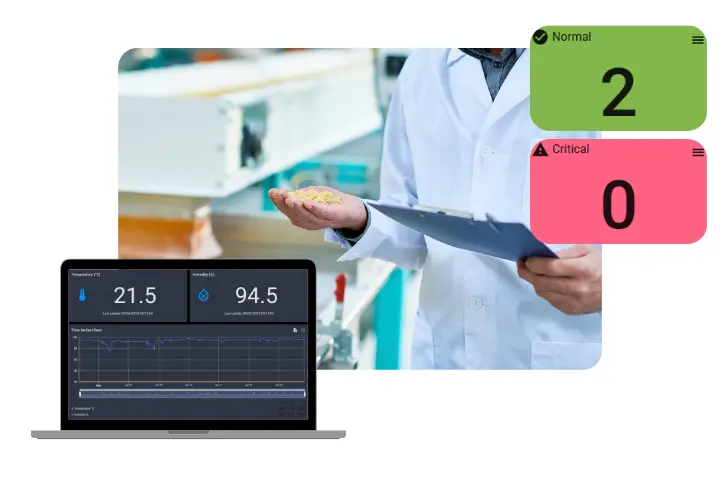
A temperature data logger is an electronic device that automatically records temperature over a set period. These devices are widely used to ensure that sensitive items such as vaccines, perishable goods, and laboratory samples remain within specific temperature thresholds.
With connectivity features like Wi-Fi or cellular, these loggers provide real-time monitoring, remote access, and automated alerts to help prevent costly losses.
Wi-Fi vs Cellular Temperature Data Loggers: Key Differences
1. Wi-Fi Temperature Data Loggers
Best For: Facilities with stable internet access, centralized monitoring, and real-time data logging.
Features:
- Transmits temperature data over a Wi-Fi network
- Stores data in the cloud or on a connected server
- Sends automatic alerts for temperature excursions via email or SMS
- Supports integration with monitoring dashboards
Advantages:
- Continuous data access from any location with internet
- Ideal for controlled environments such as hospitals, laboratories, and warehouses
- Generally lower operational costs compared to cellular options
Limitations:
- Requires a stable Wi-Fi connection
- Limited in areas with poor or no internet infrastructure
Common Applications:
Server rooms and IT facilitiese and often come with digital signatures that verify data integrity.
Vaccine refrigerators in clinics or hospitals
Climate-controlled storage rooms
2. Cellular Temperature Data Loggers
Best For: Remote locations, mobile applications, and areas without reliable internet.
Features:
- Uses a cellular network (e.g., 4G or LTE) to transmit data
- Operates independently from local internet infrastructure
- Sends real-time alerts and status updates to cloud platforms
- Can function during transport or in rural and isolated areas
Advantages:
- Does not rely on Wi-Fi or wired networks
- Ideal for transportation and logistics
- Offers consistent performance in remote or mobile environments
Limitations:
- Requires a cellular data plan (ongoing cost)
- Slightly higher initial investment compared to Wi-Fi models
Common Applications:
- Cold chain logistics and mobile refrigeration
- Monitoring in agricultural fields or remote research stations
- Maritime or cross-border transportation of sensitive goods
How to Choose the Right Temperature Data Logger
Here is a simple comparison chart to help you decide:
| Criteria | Wi-Fi Logger | Cellular Logger |
|---|---|---|
| Internet Dependency | Requires Wi-Fi | Operates via cellular network |
| Ideal Location | Fixed, indoor environments | Remote or mobile applications |
| Data Access | Cloud-based, real-time | Cloud-based, real-time |
| Setup Requirements | Requires Wi-Fi network | Requires cellular SIM and signal |
| Cost | Lower upfront and operational costs | Higher cost due to data plans |
| Monitoring During Transport | Not suitable | Highly suitable |
Key Factors to Consider
efore purchasing a temperature data logger, consider the following:
- Location of Use: Will the device operate in a fixed facility or in transit?
- Connectivity Availability: Is there a reliable Wi-Fi or cellular network available?
- Real-Time Monitoring Needs: Do you require immediate alerts or regular data logging?
- Compliance Requirements: Does your industry demand regulatory compliance?
- Power Source: Will the device run on battery or external power? Battery life is critical for remote deployments.