Ultimate Guide to Temperature Data Loggers
What is a Temperature Data Logger?
A temperature data logger is a device used to automatically measure and record temperature readings over time. It helps businesses monitor temperature-sensitive environments such as cold rooms, freezers, laboratories, and storage facilities, ensuring compliance, product safety, and accurate temperature records without manual checks.

Temperature Data Logger for Compliance
Singapore’s strict regulations from authorities like SFA (Singapore Food Agency) and HSA (Health Sciences Authority) require businesses in food, healthcare, and biotech sectors to maintain precise temperature records.
Temperature monitoring negligent incidents are evident of the importance of temperature monitoring.
TT18 4G Temperature Humidity Sensor
No setup needed, turn on the temperature data logger and deploy into your warehouse or truck to begin logging data. Access the data in real time from IOT-ezy cloud platform.
- 4G wireless connectivity
- Data storage and transmission (20,000 readings)
Brand: TZone
Model: TT18-4G-M
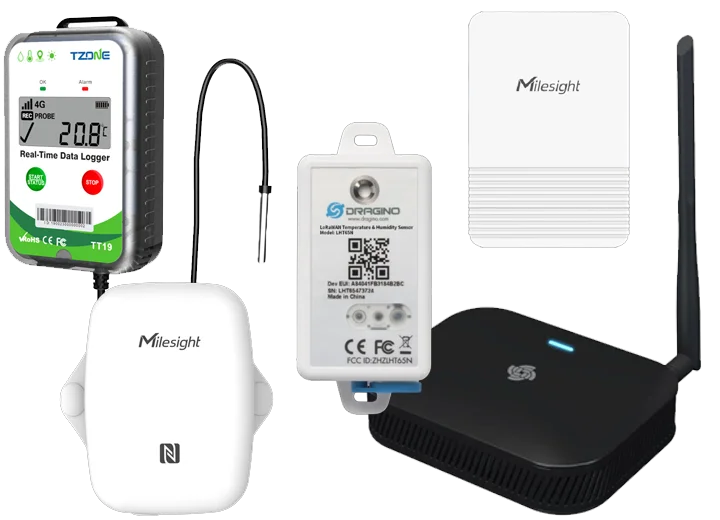
Temperature Data Loggers Products
Our temperature data loggers automate recording, send instant alerts, and generate audit-ready reports—making compliance simple and protecting your assets effortlessly.
-
D2X NB-IOT Temperature Sensor
-
Milesight EM300 LoRaWAN Temperature & Humidity Sensor
-
JT301B 4G Temperature Sensor and GPS Tracker
-
LHT65N LoRaWAN Temperature & Humidity Sensor
-
Milesight EM320 LoRaWAN Temperature & Humidity Sensor
-
TT19 4G Temperature Humidity Sensor
-
Milesight TS30X LoRaWAN Temperature Sensor
-
WF501 Wifi Temperature Logger
-
SL111A LoRaWAN Temperature & Humidity Sensor
Looking for a temperature data logger supplier in Singapore? View our range of temperature data loggers here, suitable for cold rooms, laboratories, and compliance monitoring.
Temperature Data Logger Technologies Compared: WiFi, BLE, LoRaWAN, Cellular & Sigfox
|
Technologies |
Signal Range |
Penetrative Capabilities |
Power Requirements |
Mesh Availability |
Cost to implement |
Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
WiFi |
30–100 m indoors, up to 300 m outdoors |
Poor through walls/obstacles |
High (requires AC / DC power supply usually) |
No |
Medium |
Offices, labs, small cold rooms, warehouses with good coverage |
|
BLE |
10–50 m indoors, up to 100 m outdoors |
Poor (signal easily blocked by walls/metal) |
Very low (battery can last months to years) |
Limited (requires gateway for mesh) |
High |
Portable loggers, short-range monitoring, fridges, small labs |
|
LoRaWAN |
2–10 km (urban), 10–15 km (rural) |
Moderate (penetrates walls/buildings better than WiFi/BLE) |
Very low (battery lasts years) |
Limited (some support mesh via repeaters) |
Medium |
Large warehouses, cold chain, outdoor storage, city-scale deployments |
|
Cellular (4G/LTE, NB-IoT) |
Nationwide coverage |
Good (depends on network, generally strong) |
Medium (battery can last weeks to months) |
No |
Low |
Remote locations, logistics vehicles, distributed storage facilities, pharma transport |
|
Sigfox |
10 km (urban), 50 km (rural) |
Moderate (penetrates walls moderately) |
Very low (battery lasts years) |
No |
Medium |
Large-area, low-data reporting |
Data Logger Primary Feature
Read temperature data
Log temperature data
Export data to file / cloud
Applications of Temperature Data Loggers
🧪 Pharmaceuticals & Laboratories
Monitor cold storage for vaccines, reagents, and biological samples.
🥶 Cold Chain & Logistics
Ensure consistent temperature during transportation of perishable goods.
🏥 Hospitals & Clinics
Monitor vaccine refrigerators and medication storage.
🍱 Food & Beverage
Maintain food safety in cold rooms, display chillers, and walk-in freezers.
💻 Data Centers & Server Rooms
Prevent equipment failure by tracking temperature in critical infrastructure.
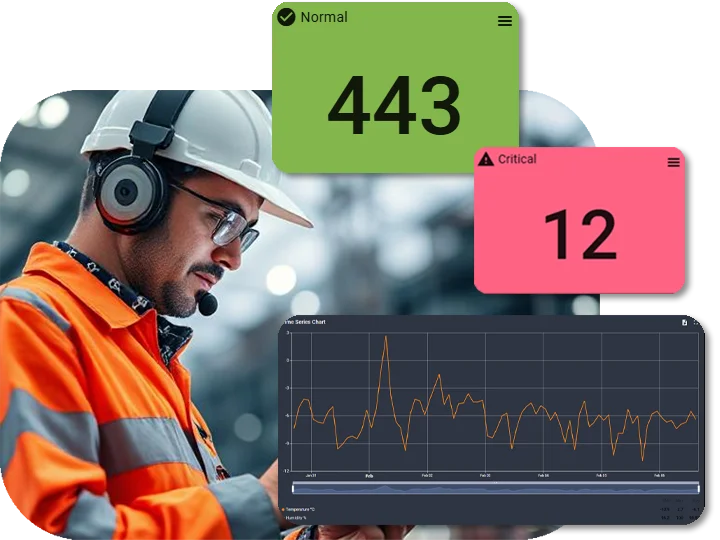
Benefits of Temperature Data Logging
Savings on manpower
Maintain product standards
Paperless for sustainability
Identify opportunities for power savings
Frequently Asked Questions
Additional Data Logging Resources
Learn more about our IoT systems
Food Safety Monitoring System
Learn More
Ready to make work easy?
Get started with IOTezy, the tech behind workflow optimization.













