What Is a LoRaWAN Temperature Sensor? Use Cases, Benefits & Examples
A LoRaWAN temperature sensor is a wireless device used to measure temperature over long distances while consuming very little power. It is commonly used in industries such as cold chain logistics, food services, healthcare, laboratories, warehouses, and agriculture, where reliable and continuous temperature monitoring is critical.
Unlike traditional wired sensors or short-range wireless devices, LoRaWAN temperature sensors are designed for long-range communication, multi-year battery life, and centralised cloud monitoring, making them ideal for large facilities or distributed sites.
In this article, we’ll explain how LoRaWAN temperature sensors work, where they are used, their benefits, limitations, and how they compare with other wireless temperature monitoring technologies.
Examples of LoRaWAN temperature sensors we carry:
What Is a LoRaWAN Temperature Sensor?
A LoRaWAN temperature sensor is a temperature-sensing device that transmits data using the LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) protocol.
It typically consists of:
– A temperature sensor (internal or external probe)
– A LoRa radio module
– A battery (often designed to last years)
– Firmware that sends data at set intervals to a LoRaWAN gateway
The data is then forwarded from the gateway to a cloud-based temperature monitoring platform, where users can view readings, receive alerts, and generate reports.
How LoRaWAN Works for Temperature Monitoring
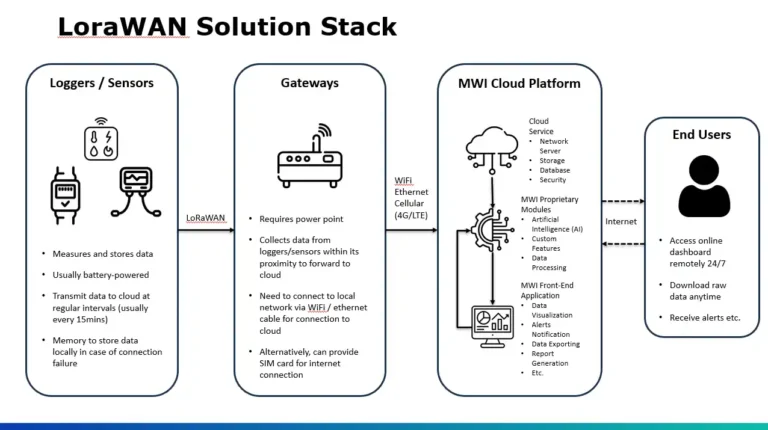
LoRaWAN is designed specifically for low-power, long-range IoT communication.
Step-by-step overview:
1. The LoRaWAN temperature sensor measures temperature at a configured interval (e.g. every 5 or 10 minutes)
2. The sensor transmits small data packets using LoRa radio signals
3. A nearby LoRaWAN gateway receives the data
4. The gateway forwards the data to a network server via the internet
5. The data is stored, visualised, and analysed in a cloud platform
Because LoRaWAN sends small, infrequent messages, power consumption is extremely low, enabling long battery life.
Key Benefits of LoRaWAN Temperature Sensors
1. Long-Range Communication
LoRaWAN sensors can transmit data:
Up to 2–5 km indoors (depending on building structure)
Up to 10–15 km outdoors
This makes them ideal for warehouses, industrial parks, farms, and multi-storey buildings.
2. Long Battery Life
Most LoRaWAN temperature sensors can operate for 3–10 years on a single battery, depending on:
Reporting frequency
Transmission power
Environmental conditions
This significantly reduces maintenance compared to WiFi or cellular sensors.
3. Reliable in Challenging Environments
LoRaWAN performs well in:
Cold rooms and freezers
Basements and plant rooms
Warehouses with metal racks
Industrial facilities
This reliability is one reason LoRaWAN temperature monitoring is widely used in cold chain applications.
4. Scalable and Cost-Effective
One LoRaWAN gateway can support hundreds to thousands of temperature sensors, making it cost-effective for large deployments.
Common Use Cases for LoRaWAN Temperature Sensors
Cold Chain Monitoring
LoRaWAN temperature sensors are widely used to monitor:
– Cold rooms
– Freezers
– Chillers
– Refrigerated storage
They help businesses comply with food safety and healthcare regulations by providing 24/7 temperature records and alerts.
Food & Beverage Industry
Restaurants, central kitchens, and food manufacturers use LoRaWAN temperature monitoring to:
– Track storage temperatures
– Detect equipment failure early
– Maintain audit-ready temperature logs
Healthcare, Pharma & Biotech
Hospitals and laboratories use LoRaWAN temperature sensors for:
– Vaccine storage
– Drug refrigerators
– Clean rooms
– Sample storage
The long battery life and reliability reduce operational risk.
Warehouses & Logistics
In large warehouses, LoRaWAN temperature sensors enable:
– Multi-zone temperature monitoring
– Coverage across wide areas
– Centralised monitoring across multiple locations
Agriculture & Smart Farming
LoRaWAN temperature sensors are used in:
– Greenhouses
– Cold storage for produce
– Environmental monitoring for crops
Indoor vs Outdoor LoRaWAN Temperature Sensors
Indoor Sensors
Typically used in:
– Cold rooms
– Warehouses
– Labs
– Commercial kitchens
They focus on accuracy and signal reliability through walls and equipment.
Outdoor Sensors
Designed for:
– Weather resistance (IP65/IP67)
– Wider temperature ranges
– Harsh environmental conditions
Used in farms, outdoor storage, and industrial sites.
Battery Life Expectations
Battery life depends on several factors:
– Reporting interval (e.g. every 5 minutes vs every 30 minutes)
– Signal strength
– Temperature extremes
– Sensor design
Typical battery life ranges:
– 3–5 years for frequent reporting
– 5–10 years for less frequent reporting
LoRaWAN temperature monitoring is ideal when frequent battery replacement is not practical.
Typical Costs of LoRaWAN Temperature Sensors

Costs vary based on sensor type and deployment scale.
Common cost components:
– Temperature sensor hardware
– LoRaWAN gateway (shared across sensors)
– Cloud monitoring platform
– Ongoing software or data fees
While the upfront cost may be higher than basic data loggers, LoRaWAN temperature sensors often deliver lower total cost of ownership due to:
– Reduced maintenance
– Fewer site visits
– Long battery life
– Centralised monitoring
LoRaWAN vs Other Temperature Monitoring Technologies
LoRaWAN vs WiFi Temperature Sensors
|
Feature |
LoRaWAN |
WiFi |
|---|---|---|
|
Range |
Long |
Short |
|
Battery life |
Years |
Months |
|
Power usage |
Very low |
High |
|
Reliability in cold rooms |
High |
Often poor |
LoRaWAN vs NB-IoT
|
Feature |
LoRaWAN |
NB-IoT |
|---|---|---|
|
SIM required |
No |
Yes |
|
Recurring costs |
Low |
Higher |
|
Battery life |
Very long |
Long |
|
Deployment |
Fast |
Carrier-dependent |
LoRaWAN vs Bluetooth
|
Feature |
LoRaWAN |
Bluetooth |
|---|---|---|
|
Range |
Kilometres |
Metres |
|
Real-time monitoring |
Yes |
Limited |
|
Infrastructure |
Gateway-based |
Phone-based |
Is a LoRaWAN Temperature Sensor Right for You?
A LoRaWAN temperature sensor is ideal if you need:
– Long-range temperature monitoring
– Minimal battery maintenance
– Reliable performance in challenging environments
– Centralised monitoring across multiple sites
It is especially suitable for businesses where temperature excursions can result in financial loss, compliance risk, or safety issues.
Final Thoughts
LoRaWAN temperature sensors have become a preferred solution for industrial and commercial temperature monitoring due to their reliability, scalability, and low operating costs.
As regulations and quality requirements become stricter, LoRaWAN-based temperature monitoring offers a future-proof way to protect assets, ensure compliance, and gain real-time visibility.




